Perseverance : how to calibrate the SuperCam analyser on the Mars rover?
The January 25, 2021

How to calibrate a device once on Mars?
Aboard the "Perseverance" rover, the SuperCam module will provide a series of reference samples to improve the accuracy of mineralogical analysis of the surface of the Red Planet.
Researchers from CIRIMAT (CNRS - Toulouse INP - Université Toulouse III Paul Sabatier), in interaction with the Raimond Castaing centre (CNRS - Université Toulouse III Paul Sabatier - Toulouse INP - INSA Toulouse) and PNF2 (CNRS) have prepared one of these calibration targets at the request of IRAP (CNRS - Université Toulouse Paul Sabatier - CNES).
The process of selection and validation of calibration targets, including those prepared by other laboratories, is published in Space Science Reviews.
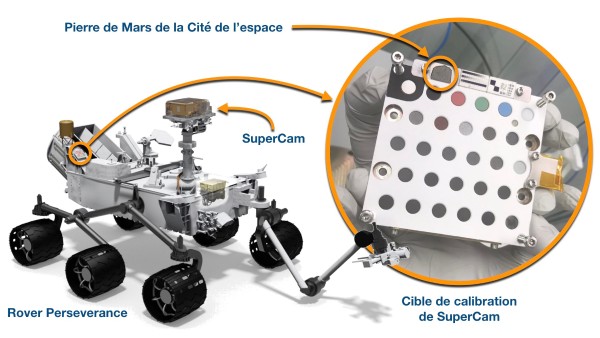
In order to take over from the Mars rover Curiosity, NASA's Mars 2020 mission is currently transporting a new rover, Perseverance, to the Red Planet. The device is equipped with the SuperCam multi-analytical module, which is more powerful than Curiosity's ChemCam. The onboard laboratory contains in particular a laser-induced plasma atomic emission spectrometer (LIBS), which is used to study Martian rocks and to search for possible traces of biological activity.
To remain accurate despite the harsh and changing conditions on Mars, the LIBS must be calibrated regularly. To do this, it takes samples designed in the laboratory with a known composition, so that reference rocks and compounds can be analysed under identical conditions. A total of thirty-six different calibration pads are installed on a sample holder designed in Spain, and the LIBS analyser will be able to select the relevant targets according to the rocks analysed.
Read the full article on the INC-CNRS website (Fr)
Credit : Cité de l’espace/NASA/Sylvestre Maurice



